曾彪彪的个人网站
首页
文章列表
>>
文章详情
马拦过河卒 - 动态规划入门
作者:
曾彪彪
日期:
2025-09-08 00:37:09
阅读(548)
分类:
问题记录
Algorithm
# P1002 [NOIP 2002 普及组] 过河卒 ## 题目描述 棋盘上 $A$ 点有一个过河卒,需要走到目标 $B$ 点。卒行走的规则:可以向下、或者向右。同时在棋盘上 $C$ 点有一个对方的马,该马所在的点和所有跳跃一步可达的点称为对方马的控制点。因此称之为“马拦过河卒”。 棋盘用坐标表示,$A$ 点 $(0, 0)$、$B$ 点 $(n, m)$,同样马的位置坐标是需要给出的。 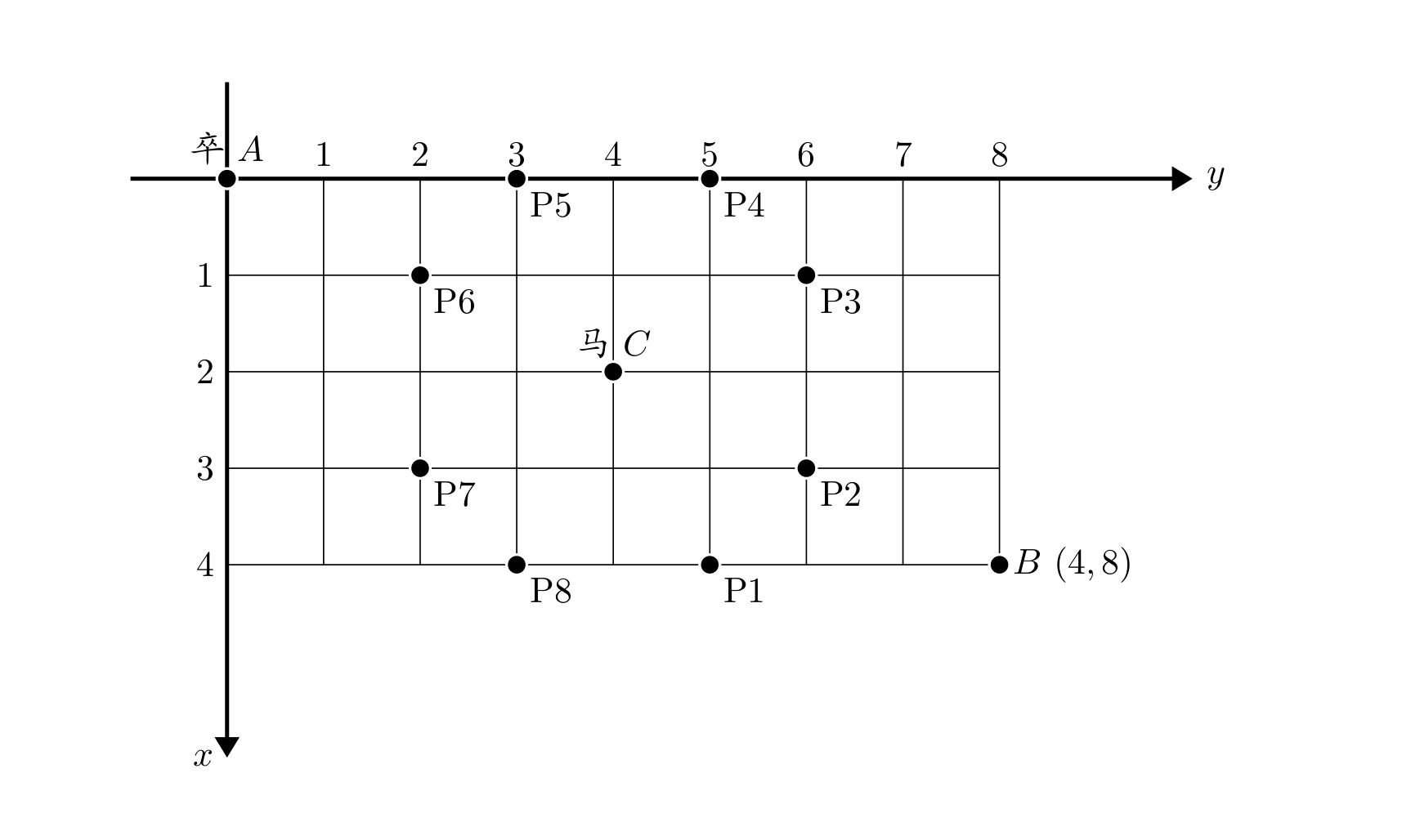 现在要求你计算出卒从 $A$ 点能够到达 $B$ 点的路径的条数,假设马的位置是固定不动的,并不是卒走一步马走一步。 ## 输入格式 一行四个正整数,分别表示 $B$ 点坐标和马的坐标。 ## 输出格式 一个整数,表示所有的路径条数。 ## 输入输出样例 #1 ### 输入 #1 ``` 6 6 3 3 ``` ### 输出 #1 ``` 6 ``` ## 说明/提示 对于 $100 \%$ 的数据,$1 \le n, m \le 20$,$0 \le$ 马的坐标 $\le 20$。 **【题目来源】** NOIP 2002 普及组第四题 --- 这题刚开始使用递归来实现,只能得60分,因为递归太深,会爆栈。代码如下: ```c++ /** start time: 8:45 End time: Type: simulator Solution: list all location can't be reached dfs(x,y) - - - test case: - - - - first submit score: 100 cause: **/ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int bx, by, cx, cy; vector<vector<bool>> grid(25, vector<bool>(25, false)); int ans = 0; void dfs(int x, int y) { if (x == bx && y == by) { ans++; return; } if (x > bx || y > by) { return; } if (grid[x][y]) { return; } dfs(x + 1, y); dfs(x, y + 1); } int main() { // freopen("C:/Users/zengsam/Downloads/P1042_2.in", "r", stdin); cin >> bx >> by >> cx >> cy; vector<int> dx = {2, 2, -2, -2, 1, 1, -1, -1}; vector<int> dy = {1, -1, 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2}; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { int lx = cx + dx[i]; int ly = cy + dy[i]; if (lx >= 0 && ly >= 0) { grid[lx][ly] = true; } } grid[cx][cy] = true; if (grid[0][0] || grid[bx][by]) { cout << 0; return 0; } dfs(0, 0); cout << ans; return 0; } ``` 后来想到了动态规划,之前学过一点点,正好能用到。代码如下: ```c++ /** start time: 8:45 End time: Type: simulator Solution: list all location can't be reached dfs(x,y) - - - test case: - - - - first submit score: 100 cause: **/ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int bx, by, cx, cy; vector<vector<bool>> grid(25, vector<bool>(25, false)); vector<vector<long long>> dp(25, vector<long long>(25, 0)); int main() { // freopen("C:/Users/zengsam/Downloads/P1042_2.in", "r", stdin); cin >> bx >> by >> cx >> cy; bx += 2; by += 2; cx += 2; cy += 2; vector<int> dx = {0, 2, 2, -2, -2, 1, 1, -1, -1}; vector<int> dy = {0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2}; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { int x = cx + dx[i]; int y = cy + dy[i]; grid[x][y] = true; } dp[2][1] = 1; for (int i = 2; i <= bx; i++) { for (int j = 2; j <= by; j++) { if (grid[i][j]) { dp[i][j] = 0; } else { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] + dp[i][j - 1]; } } } cout << dp[bx][by]; return 0; } ``` 后来看一位大佬写的代码,动态规划还能优化,将dp由二维改成一维,代码如下: ```c++ /** start time: 8:45 End time: Type: simulator Solution: list all location can't be reached dfs(x,y) - - - test case: - - - - first submit score: 100 cause: **/ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int bx, by, cx, cy; vector<vector<bool>> grid(25, vector<bool>(25, false)); vector<long long> dp(25, 0); int main() { // freopen("C:/Users/zengsam/Downloads/P1042_2.in", "r", stdin); cin >> bx >> by >> cx >> cy; bx += 2; by += 2; cx += 2; cy += 2; vector<int> dx = {0, 2, 2, -2, -2, 1, 1, -1, -1}; vector<int> dy = {0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 2, -2, 2, -2}; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { int x = cx + dx[i]; int y = cy + dy[i]; grid[x][y] = true; } dp[2] = 1; for (int i = 2; i <= bx; i++) { for (int j = 2; j <= by; j++) { if (grid[i][j]) { dp[j] = 0; } else { dp[j] = dp[j - 1] + dp[j]; } } } cout << dp[by]; return 0; } ``` 这里的一维数组dp,存储了到目前为止,可能的路径。在dp[j]未计算之前,dp[j]存储的是i-1行时的路径,如果计算d[j]+=d[j-1],那么就是计算当前行i,对应的可能路径。
评论(0)
评论(必填)
名称(必填)
联系方式(可选)
验证码(必填)
提交
评论(必填)
名称(必填)
联系方式(可选)
验证码(必填)